Probability Theory
Probability theory helps us understand how likely it is that something will happen.
簡要介紹
Probability theory is all about figuring out how likely different events are. It's used to predict outcomes in situations where things aren't certain, like guessing whether it will rain tomorrow or how likely you are to win a game. Think of it as a way to measure uncertainty and make informed decisions!
主要說明
Events and Outcomes
First, we need to understand what an 'event' is. An event is simply something that can happen, like flipping a coin and getting heads. The possible results of an event are called 'outcomes'. So, when you flip a coin, the possible outcomes are heads or tails. 🪙
Calculating Probability
Probability is calculated by dividing the number of ways a specific event can happen by the total number of possible outcomes. For example, if you want to know the probability of flipping heads, there's only 1 way to get heads, and there are 2 possible outcomes (heads or tails). So, the probability is 1/2, or 50%. ➗
Probability Scale
Probabilities are always between 0 and 1. A probability of 0 means the event is impossible (like flipping a coin and getting purple). A probability of 1 means the event is certain to happen (like the sun rising tomorrow). Anything in between represents varying degrees of likelihood. 0️⃣-1️⃣
Independent Events
Some events don't affect each other. These are called independent events. For example, if you flip a coin twice, the result of the first flip doesn't change the probability of getting heads or tails on the second flip. Each flip is a fresh start! 🔄
Dependent Events
Other events *do* affect each other. Imagine you have a bag with 5 red balls and 5 blue balls. If you pick a red ball and don't put it back, the probability of picking another red ball changes because there are now fewer red balls in the bag. ⚽️
範例
- Imagine you're baking cookies 🍪. You want to know the probability of pulling out a chocolate chip cookie from the batch. If half the cookies are chocolate chip, the probability is 50%.
- Think about a lottery 🎫. The probability of winning the jackpot is extremely low because there are so many possible combinations of numbers. That's why it's often described as 'winning the lottery' when something unlikely happens.
- Consider rolling a six-sided die 🎲. The probability of rolling a '3' is 1/6 because there's only one '3' on the die, and there are six possible numbers you could roll.
費曼AI如何引導你學習
- 選擇任意概念: 從你想掌握的主題開始——瀏覽精選學科或自行輸入。
- 先學核心要點: 用清楚、結構化的解說快速建立知識框架,掌握關鍵與常見誤區。
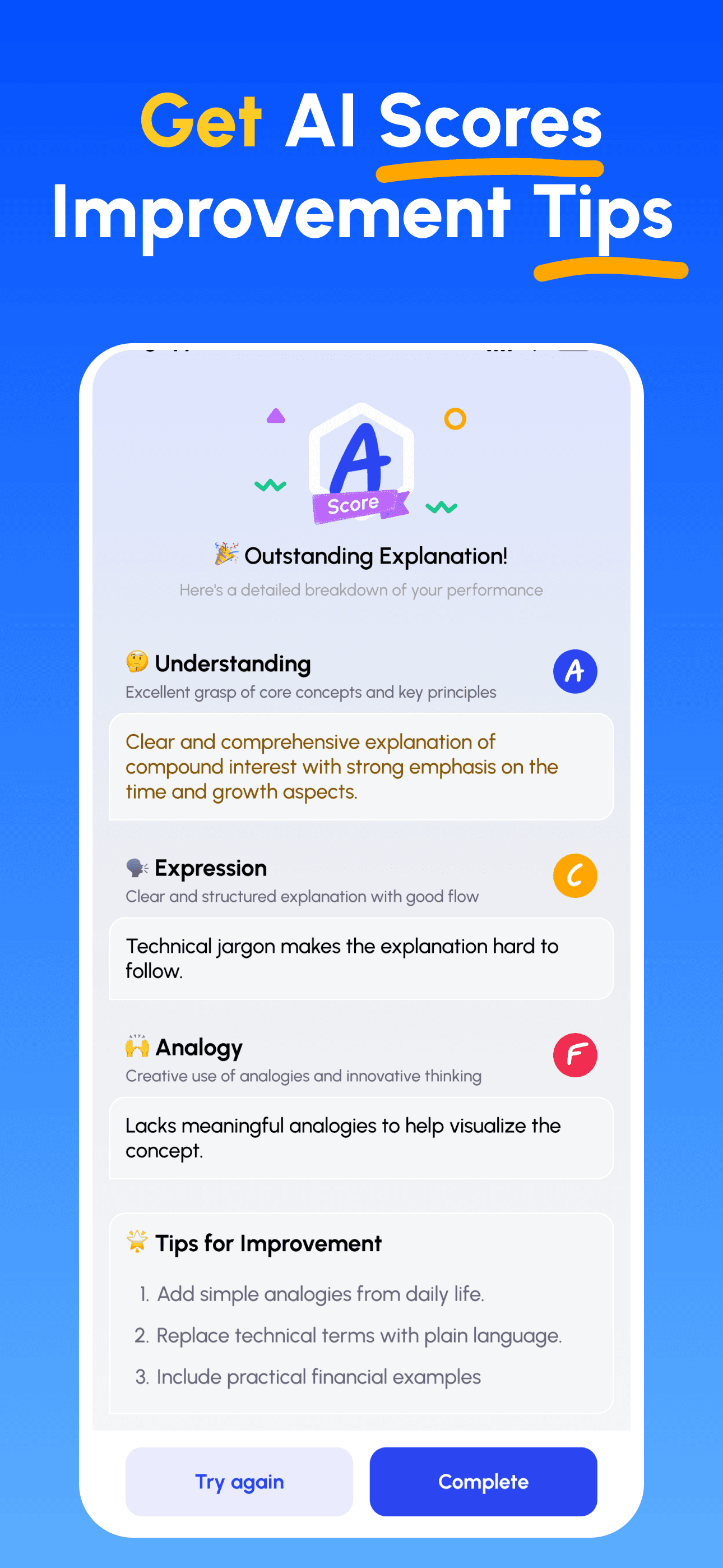
- 講解並獲得回饋: 以語音或文字錄製你的講解;立即取得在深度、清晰度、結構與示例上的分析。
- 檢視評分並精進: 依據針對性建議修正並再講解,直到能簡單講清楚為止。
立即下載費曼AI
今天就開始提升溝通能力的旅程!