Use Cases | Feynman AI
See how students, exam takers, self‑learners, and knowledge workers use the Feynman Technique with AI feedback to learn faster, explain clearly, and retain longer.
Who Benefits
Use Feynman AI to master concepts and communicate clearly.
StudentsExam PrepSelf-LearnersKnowledge Workers
- StudentsBuild strong understanding in STEM and humanities with guided explanations.Outcomes:
- From notes to clear, structured explanations.
- Deeper grasp of fundamentals and tricky edge cases.
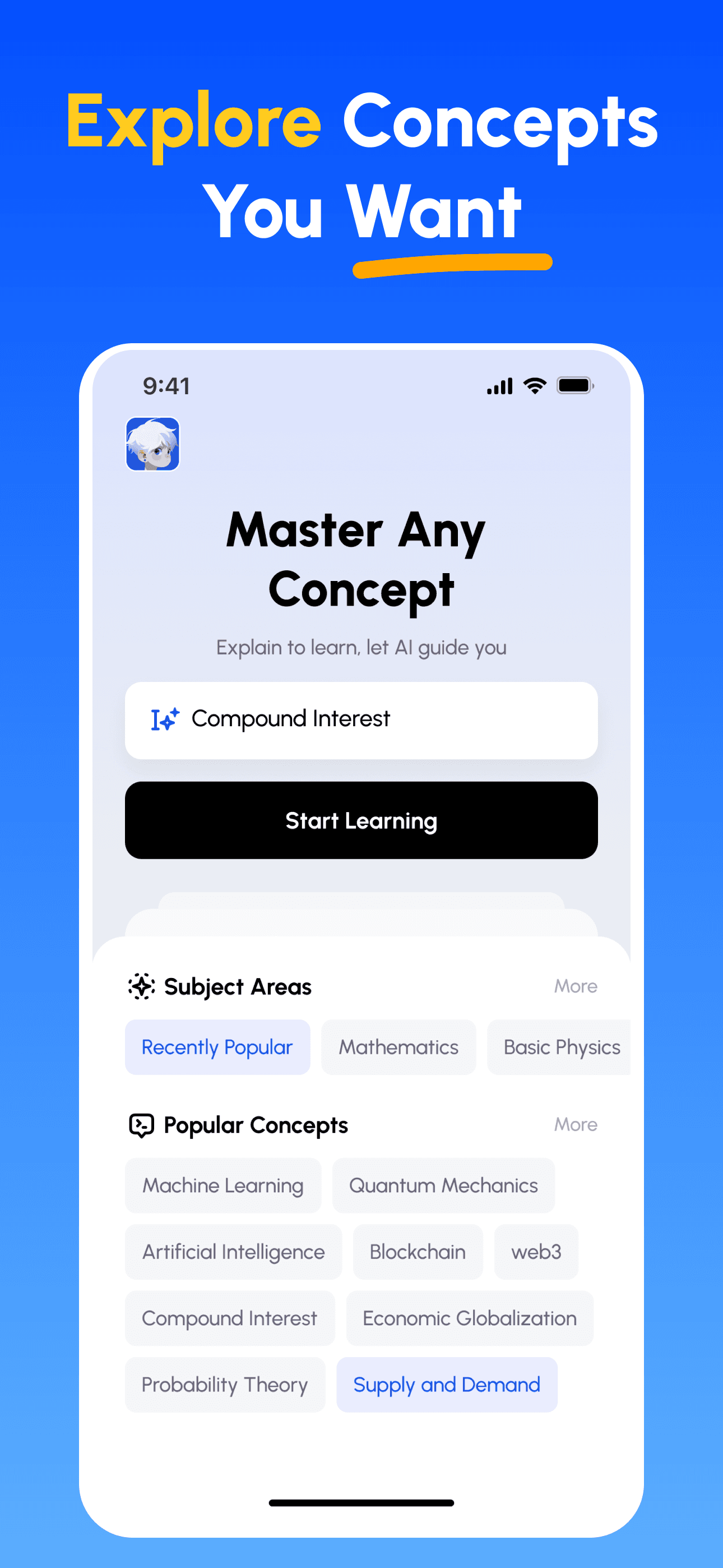
How To Use Feynman AI:- Pick a concept from the library and skim essentials.
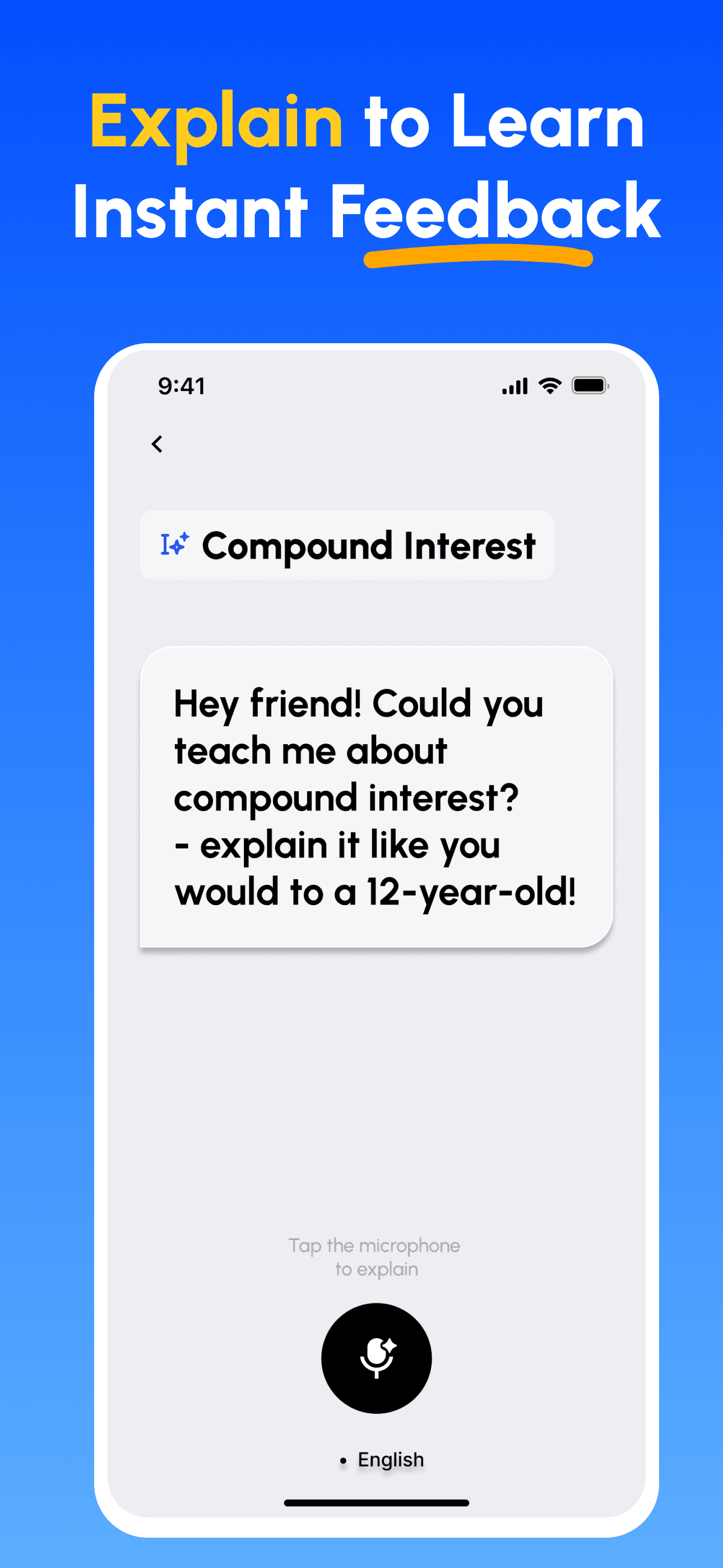
- Explain in 60–120 seconds as if teaching a classmate.
Pro Tips:One core idea per attempt. - Exam PrepPractice structured, concise explanations and improve answer quality.Outcomes:
- Stronger answer structure and clarity.
- Faster recall under time pressure.
How To Use Feynman AI:- Create topics aligned to your syllabus.
- Practice 60–120s explanations (What → How → Why).
Pro Tips:Use a three‑part pattern: definition → mechanism → example/boundary. - Self-LearnersAccelerate learning across new topics with immediate feedback.Outcomes:
- Faster ramp‑up on unfamiliar domains.
- Check real understanding via explanation.
How To Use Feynman AI:- Create topics from MOOC notes, papers or books.
- Follow AI outline → explain → analyze → refine.
Pro Tips:Anchor abstractions to real work or life examples. - Knowledge WorkersExplain complex ideas clearly in professional settings.Outcomes:
- Clearer explanations that build alignment and trust.
- More structured, persuasive docs and presentations.
How To Use Feynman AI:- Create topics for projects, proposals or features.
- Explain for a non‑expert audience in plain language.
Pro Tips:Lead with ‘why/value’, then ‘how/details’.
What You’ll Achieve
- Deep understanding by explaining, not just reading.
- Instant gap‑finding with targeted AI feedback.
- Clearer communication and structured thinking.
- Long‑term retention and transferable knowledge.
How It Works For You
- Choose a topic or create your own.
- Skim essentials to build a mental model.
- Explain in voice or text to activate recall.
- Review AI analysis and suggestions.
- Refine and track progress over time.
Common Scenarios
- Pre‑exam review and answer practice.
- Project briefings and cross‑team alignment.
- MOOCs and self‑directed upskilling.
- Interview prep and knowledge checks.