Simple Circuits
A simple circuit is a closed path that lets electricity flow from a power source through things and back again.
간단 소개
Think of a simple circuit like a circular track where electricity runs, similar to water flowing through a loop of pipes. It needs three basic things: a power source (like a battery), a path for electricity to flow (wires), and something that uses the electricity (like a light bulb). This setup allows us to power everything from flashlights to toys. 🔋
주요 설명
The Power Source 🔋
Every circuit needs something to push electricity around, like a battery or solar cell. It's like a pump that pushes water through pipes - the battery pushes electricity through wires. A 1.5V battery in a flashlight is a perfect example.
The Pathway ⚡
Wires in a circuit are like pipes for electricity. Just as water needs an unbroken pipe to flow, electricity needs a complete path to travel. If there's a break anywhere, like when you flip a light switch off, the circuit is 'open' and won't work.
The Load 💡
Something needs to use the electricity - this is called the load. It could be a light bulb, motor, or speaker. It's like putting a water wheel in a stream - it uses the flowing energy to do something useful.
The Complete Loop 🔄
Electricity must flow in a complete circle, from the power source, through the load, and back to the power source. If any part is disconnected, just like a broken circle, the circuit won't work.
예시
- A battery-powered flashlight: When you flip the switch, you complete the circuit, connecting the battery to the bulb through metal contacts, making the bulb light up. 🔦
- A doorbell circuit: Pressing the button connects the wires, completing the circuit and making the bell ring. When you release it, the circuit breaks and the ringing stops. 🔔
- A desk lamp: Plugging it in connects it to house power, and the switch creates or breaks the circuit to turn the light on or off. 💡
3단계로 모든 과목 마스터하기
- 학습 목표 선택: 이공계, 비즈니스, 인문학, 전문 기술 등 수백 가지 개념 중에서 선택하세요. 복잡한 주제를 관리하기 쉬운 단위로 분해합니다.
- 가르치면서 배우기: AI 기반 플랫폼을 사용하여 다른 사람을 가르치듯이 개념을 설명하세요. 지식의 격차를 즉시 발견하고 보완합니다.
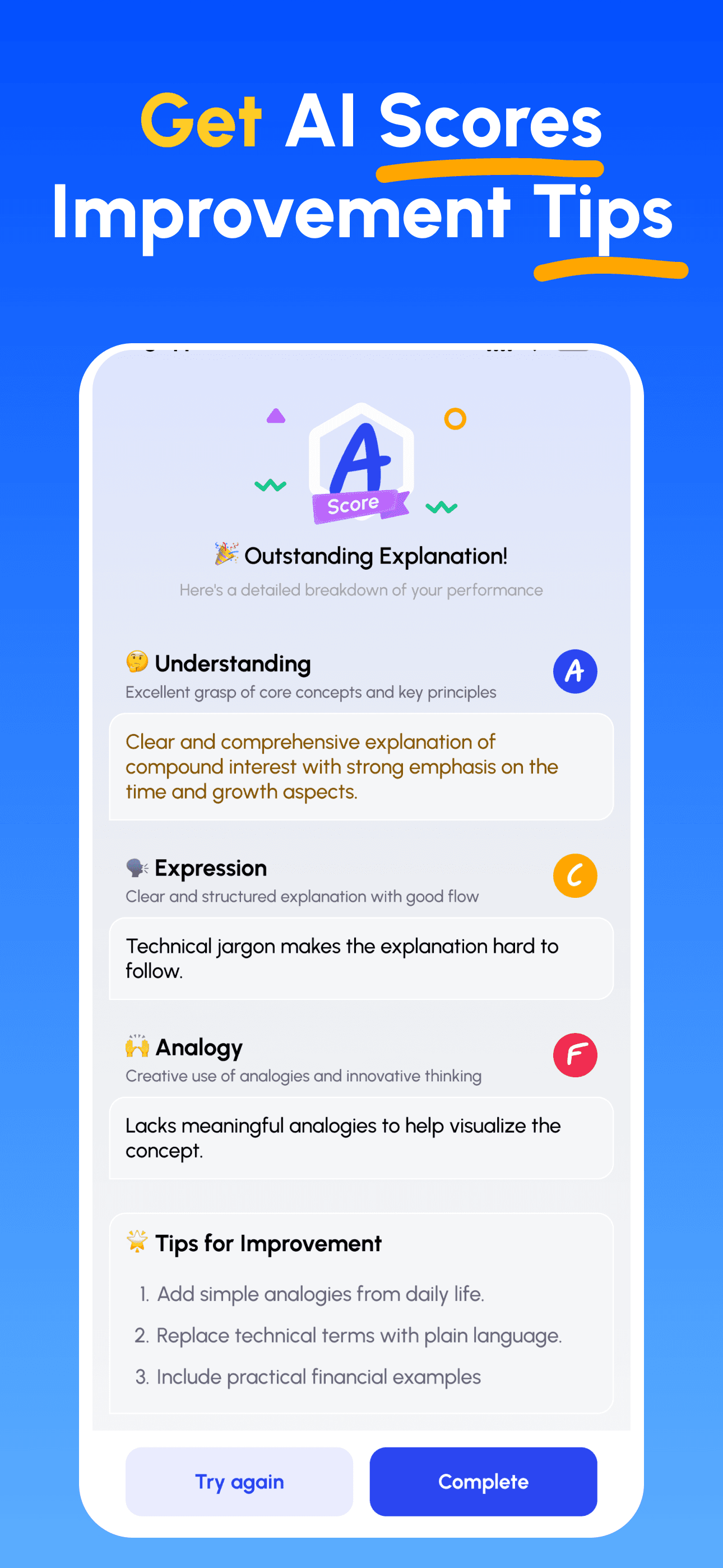
- AI 전문가 가이드 받기: 이해도, 설명의 명확성, 실제 적용 능력에 대한 즉각적이고 상세한 피드백을 받으세요.
- 점수 확인 및 개선: 타깃 팁을 따르고 설명을 다듬어, 간단히 가르칠 수 있을 때까지 반복하세요.
지금 파인만 AI 다운로드
더 나은 커뮤니케이션을 위한 여정을 오늘 시작하세요!