Physical Changes
A physical change happens when something changes how it looks but stays the same thing inside, like water turning into ice.
Brief Introduction
Physical changes are like giving something a makeover - the outside appearance might change, but what it's made of stays exactly the same. 🔄 Think of it like rearranging furniture in your room - the room looks different, but you still have all the same furniture. These changes can usually be reversed, just like how you can melt ice back into water.
Main Explanation
No New Substances 🎨
During a physical change, no new substances are created. It's like folding a paper airplane - whether flat or folded, it's still paper. The material's chemical makeup stays exactly the same.
Reversible Changes ⏪
Most physical changes can be undone. It's like a LEGO creation - you can build it up and take it apart, but the LEGO pieces remain the same. Examples include freezing and melting, or dissolving salt in water.
Observable Changes 👀
Physical changes affect properties like shape, size, or state. It's like cutting your hair - the appearance changes, but it's still hair. Changes might include color, texture, or form, but the substance remains unchanged.
Energy Involvement 💫
Physical changes might need energy to happen, but they don't create new chemical bonds. Like heating water to make steam - it needs energy, but it's still H2O, just in a different form.
Examples
- Crushing an aluminum can: The can changes shape and size, but it's still made of aluminum! 🥤
- Making a snowball: You're just packing snow into a different shape - when it melts, it's still water ⛄
- Shredding paper: The paper pieces are smaller, but they're still paper - just in a different form 📄
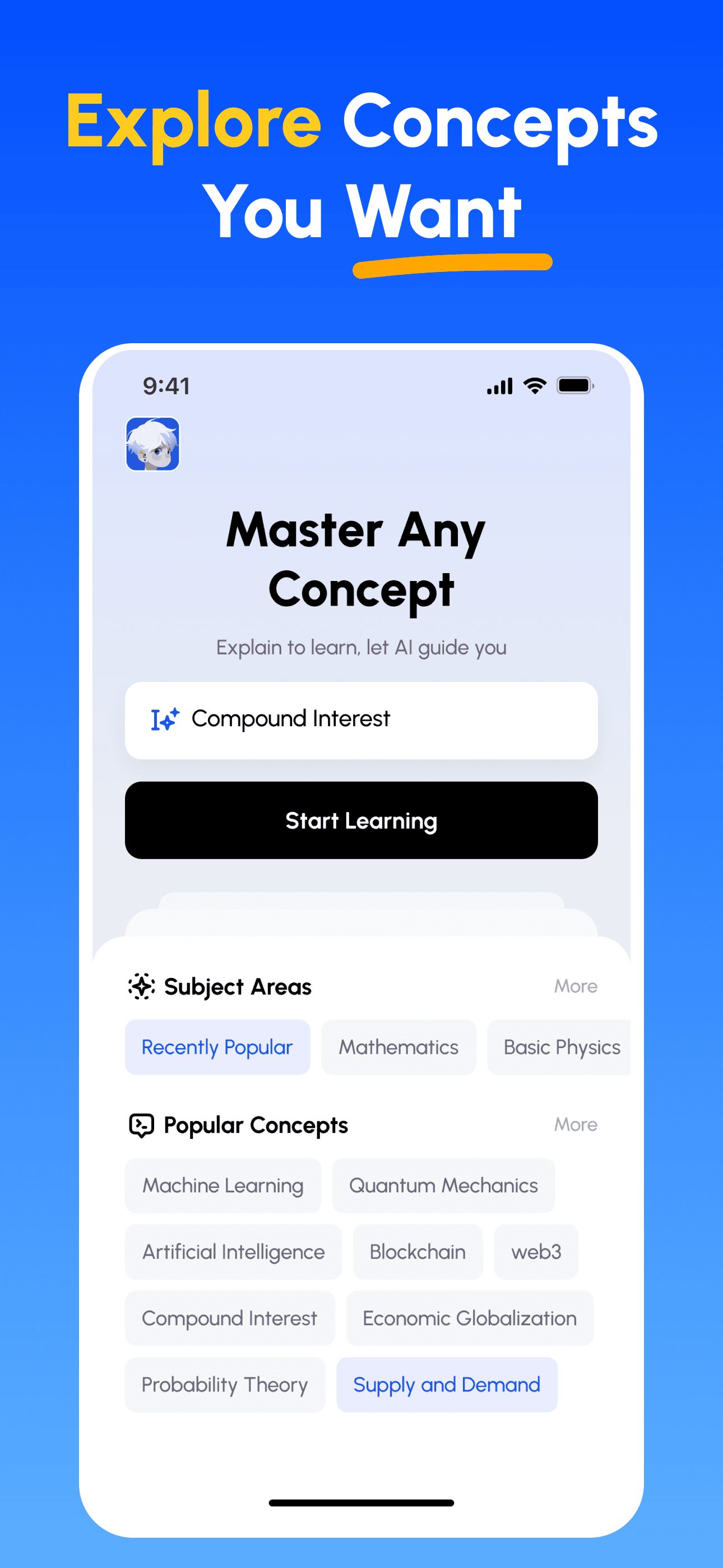
How Feynman AI Guides Your Learning
- Choose Any Concept: Start from a topic you want to master — browse curated subjects or enter your own.
- Learn Essentials: Skim clear, structured explanations, key terms and common pitfalls to form a solid mental model.
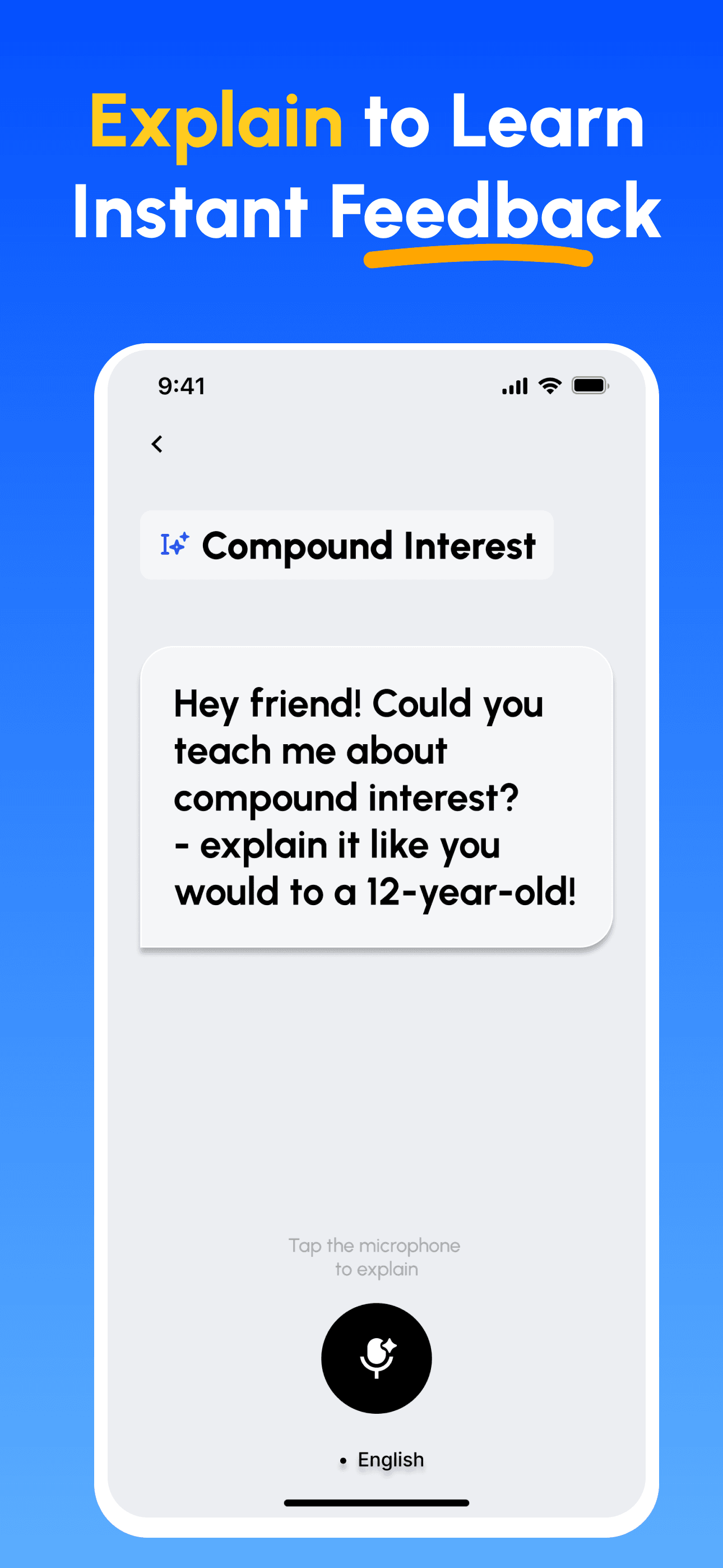
- Explain & Get Feedback: Record your explanation (voice or text). Get instant analysis on depth, clarity, structure and example quality.
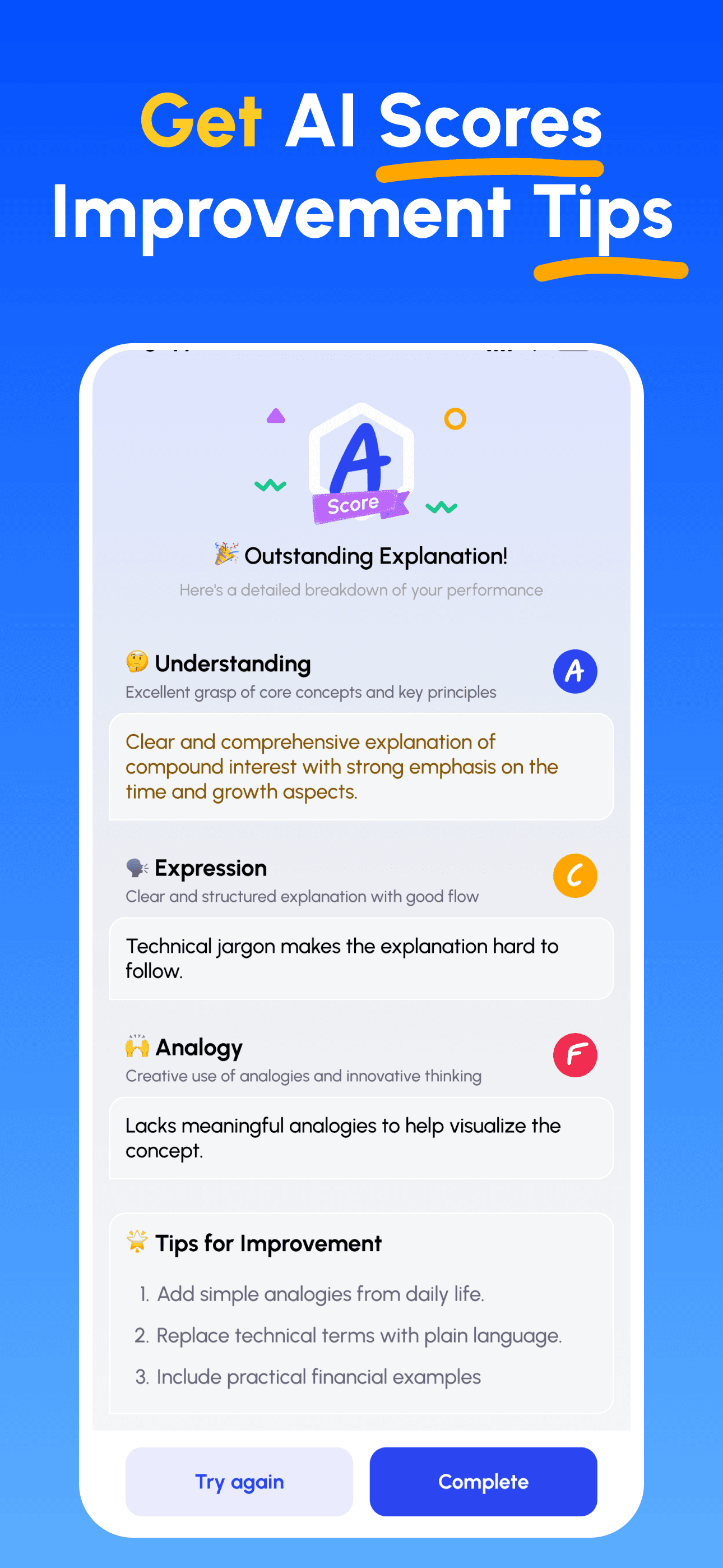
- Review Scores & Improve: Follow targeted tips, refine your explanation and iterate until you can teach it simply.
Download Feynman AI Now
Start your learning journey today!