Heat Transfer
Heat transfer is the movement of warmth from warmer things to cooler things, like a hot cup of coffee cooling down. 🌡️
Brief Introduction
Heat transfer is how warmth moves naturally from hot objects to colder ones, always trying to reach a balanced temperature. 🌡️ It's something we experience every day, from cooling our food to warming our hands by a fire. This process explains why ice melts in your drink and why a warm blanket keeps you cozy on a cold night.
Main Explanation
Conduction 🤝
It's like passing a message down a line of people - heat moves through direct contact. When you touch a hot pan, heat travels directly from the pan to your hand. Similarly, a metal spoon in hot soup becomes hot because heat travels along the spoon.
Convection 🌊
It's like how hot air balloons rise - warm fluids (liquids or gases) naturally move upward while cool ones sink down. This is why hot air rises to your ceiling and why warm water rises to the top of your bath.
Radiation ☀️
It's like feeling the warmth of the sun on your face - heat travels through space without needing anything in between. This is how the sun warms the Earth and how a campfire warms people sitting around it.
Examples
- When you make hot chocolate, the metal spoon gets hot because of conduction, the milk swirls as it heats due to convection, and your hands feel warm holding the mug through radiation. ☕
- On a cold day, a window feels cold through conduction, warm air rises to the ceiling through convection, and a fireplace warms the room through radiation. 🏠
- At the beach, the sand feels hot through conduction, sea breezes form through convection, and the sun warms your skin through radiation. 🏖️
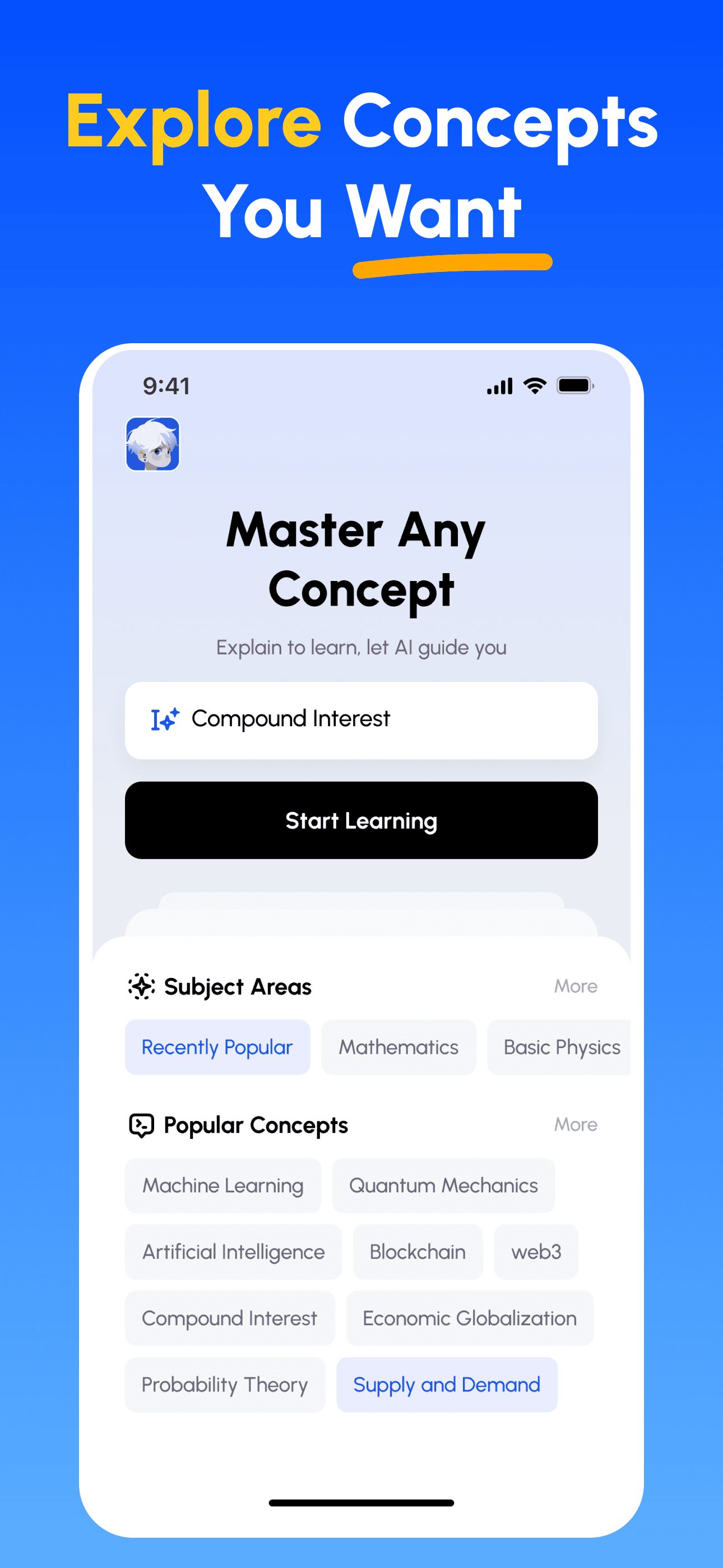
How Feynman AI Guides Your Learning
- Choose Any Concept: Start from a topic you want to master — browse curated subjects or enter your own.
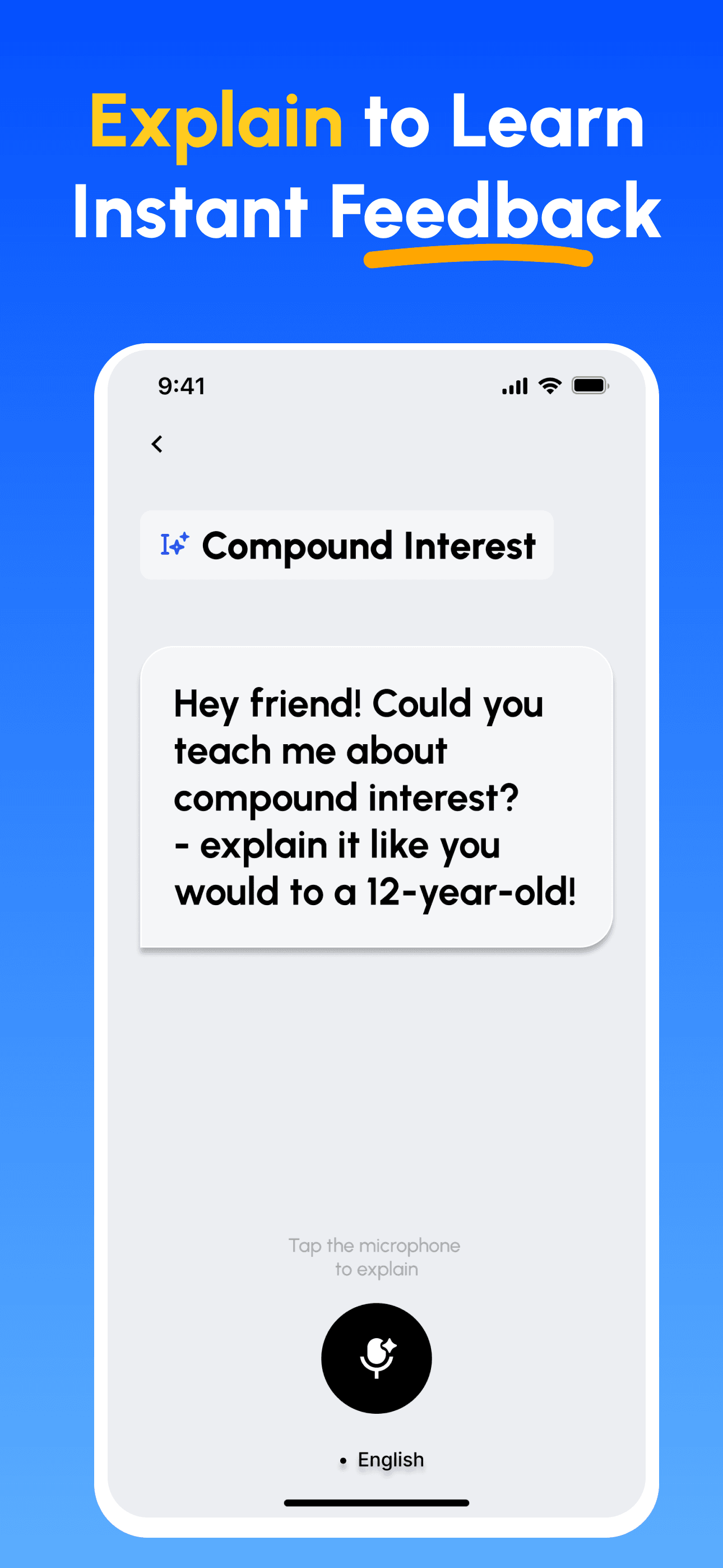
- Learn Essentials: Skim clear, structured explanations, key terms and common pitfalls to form a solid mental model.
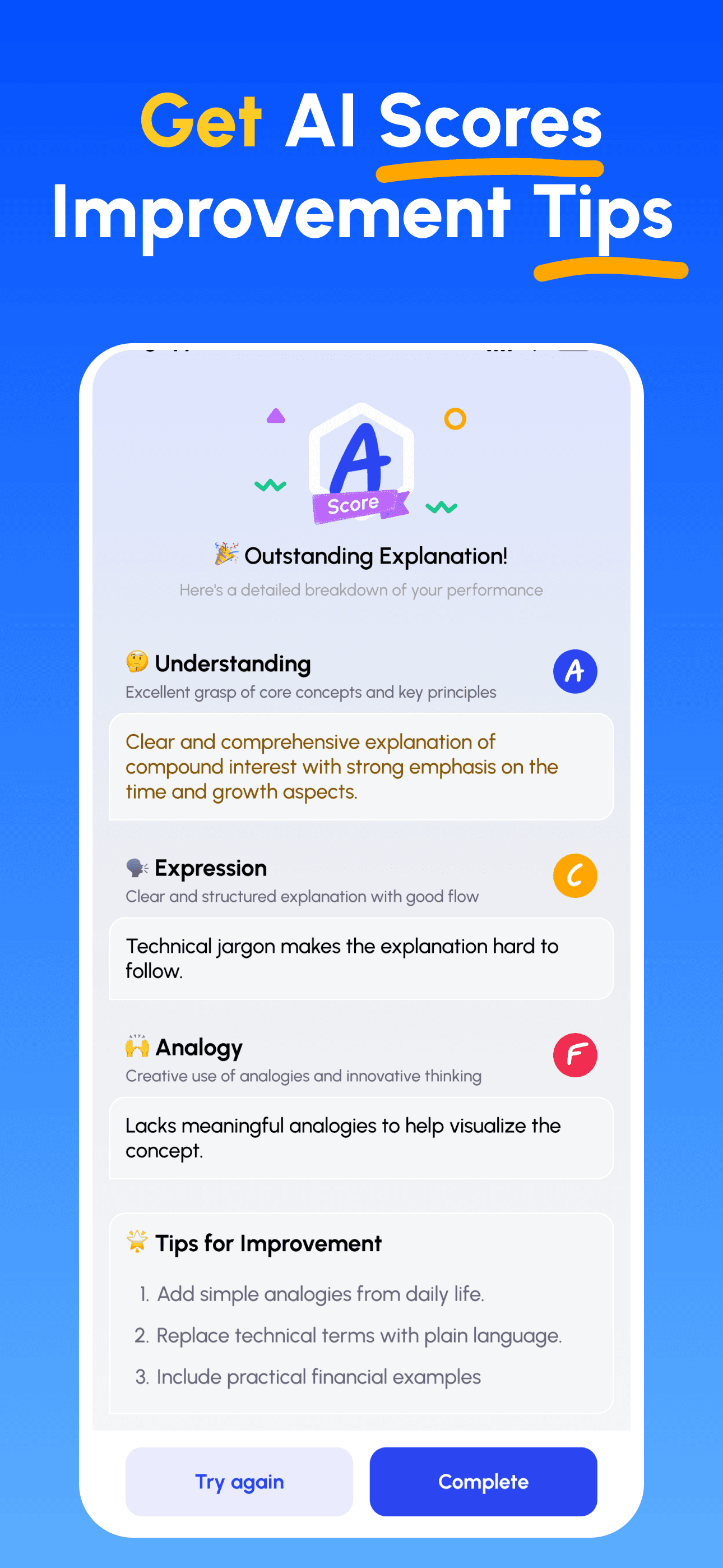
- Explain & Get Feedback: Record your explanation (voice or text). Get instant analysis on depth, clarity, structure and example quality.
- Review Scores & Improve: Follow targeted tips, refine your explanation and iterate until you can teach it simply.
Download Feynman AI Now
Start your learning journey today!