Food Chain
A food chain shows how different living things eat each other to get energy, like a dinner line in nature. 🌿🦌🐯
Brief Introduction
A food chain is nature's way of showing who eats whom in an ecosystem. It's like a restaurant menu that tells us how energy moves from one living thing to another, starting with plants that get energy from the sun. Just as we need to eat to survive, every creature in nature is part of this eating pattern, creating a chain of energy transfer.
Main Explanation
Starting with Producers 🌱
The food chain always begins with plants (producers). It's like having a solar power plant - plants use sunlight to make their own food through photosynthesis, starting the energy flow in the chain.
Primary Consumers 🐰
Next come plant-eaters (herbivores). Think of them like vegetarians at a restaurant - rabbits eating grass, deer eating leaves, or caterpillars eating plants.
Secondary Consumers 🦊
Then we have animals that eat the plant-eaters. It's like the next table at the restaurant - foxes eating rabbits, or birds eating insects.
Top Predators 🦁
At the top are the big predators. They're like the VIP diners who aren't eaten by anyone else - lions, eagles, or sharks in their environments.
Examples
- Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk: Like passing a baton in a relay race, each animal passes energy to the next. 🌾🦗🐸🐍🦅
- Algae → Small Fish → Bigger Fish → Seal: Think of it as small sushi being eaten by bigger sushi, ending with a seal's feast! 🌊🐟🐠🦭
- Plant → Caterpillar → Robin → Cat: Similar to a sandwich being eaten by a bird, which then becomes a cat's dinner. 🌿🐛🐦😺
How Feynman AI Guides Your Learning
- Choose Any Concept: Start from a topic you want to master — browse curated subjects or enter your own.
- Learn Essentials: Skim clear, structured explanations, key terms and common pitfalls to form a solid mental model.
- Explain & Get Feedback: Record your explanation (voice or text). Get instant analysis on depth, clarity, structure and example quality.
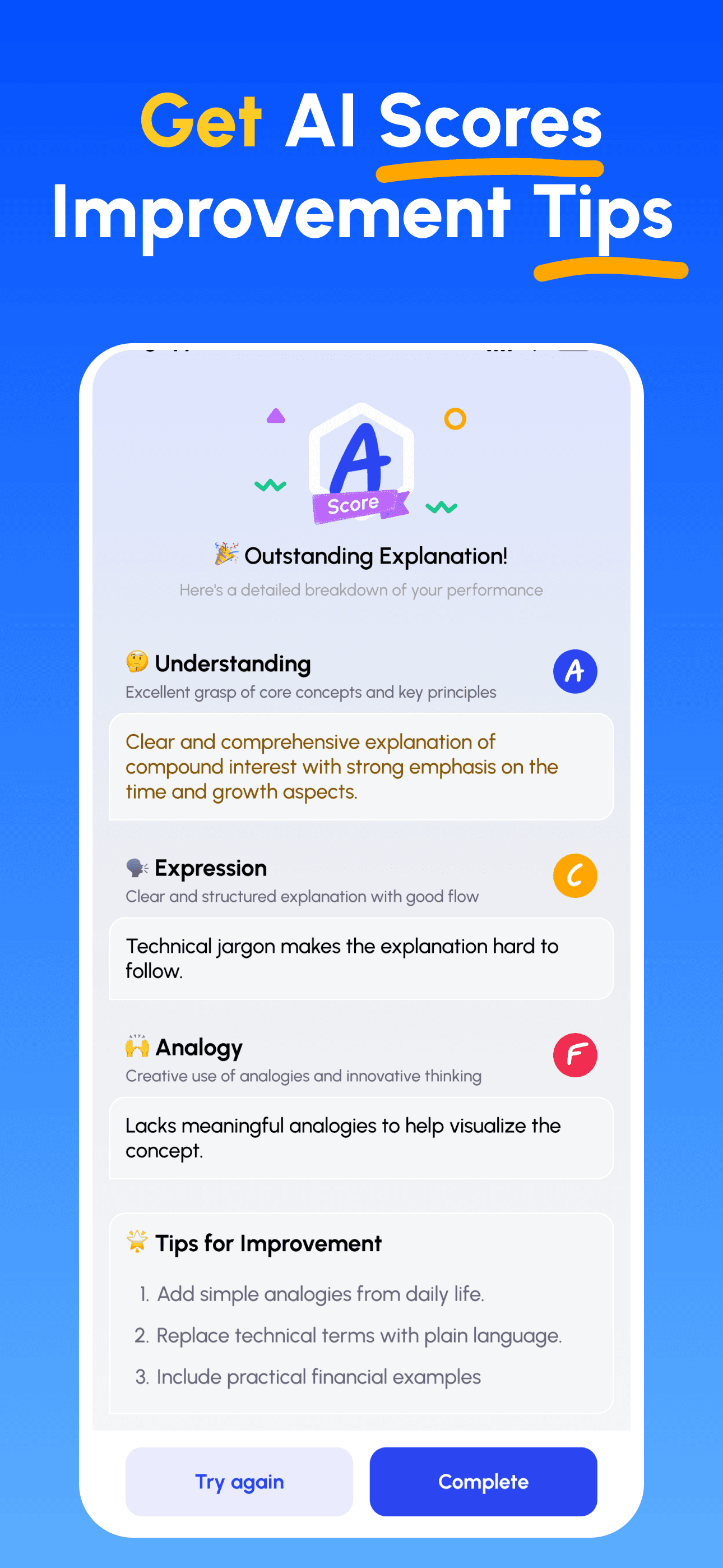
- Review Scores & Improve: Follow targeted tips, refine your explanation and iterate until you can teach it simply.
Download Feynman AI Now
Start your learning journey today!