Cryptography
Cryptography is the art of keeping messages secret by turning them into codes that only intended people can read. 🔐
概要
Just like how you might use a secret language with your best friend, cryptography is about protecting information from others. 🤫 It's used everywhere in our digital world, from sending text messages to making online purchases. Think of it as putting your message in a super-secure locked box where only the person with the right key can open it.
詳細説明
Making Messages Secret 📝
It's like having a special decoder ring from a cereal box, but much more complex. When you type a message, cryptography scrambles it into something that looks like gibberish. Only someone with the right 'decoder ring' (called a key) can unscramble it.
Keys and Locks 🔑
Just like your house has locks and keys, cryptography uses digital keys. Sometimes you use the same key to lock and unlock (like your house key), and sometimes you use different keys (like a public key to send messages and a private key to read them).
Protecting Information 🛡️
It's like putting your diary in a safe. When you shop online, cryptography protects your credit card number. When you use social media, it keeps your password secure. It's working behind the scenes to keep your digital life private.
例題
- When you see the little padlock 🔒 symbol in your web browser while shopping online, that's cryptography making sure your credit card information stays safe.
- Writing a message like 'HELLO' as 'IFMMP' by shifting each letter forward by one is a simple form of cryptography - just like secret codes kids use in games.
- WhatsApp's 'end-to-end encryption' is like putting your message in a magical envelope that can only be opened by your friend's phone - even WhatsApp can't read it! 📱
3ステップで確実に習得
- 学習目標を設定: 理系、ビジネス、文系、専門スキルなど、数百の概念から選択。複雑なトピックを理解しやすい単位に分解します。
- 教えることで学ぶ: AI搭載プラットフォームを使用して、他者に教えるように概念を説明。知識のギャップを即座に発見し、補完します。
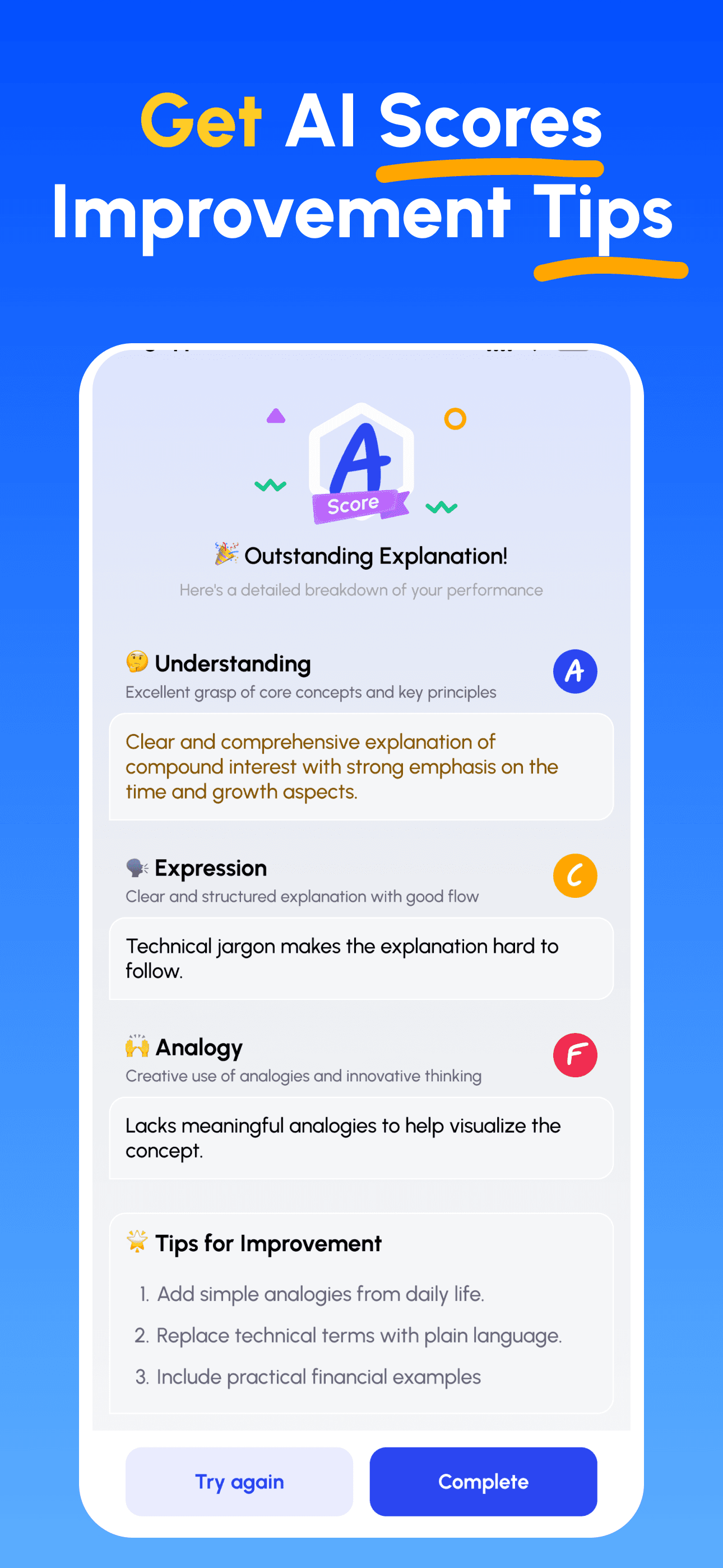
- AIエキスパートガイダンス: 理解度、説明の明確さ、実践的応用力について、即時の詳細なフィードバックを受け取ります。
- スコアを確認して改善: 的確なヒントに従い、説明を磨き、シンプルに教えられるまで反復します。
ファインマンAIを今すぐダウンロード
より良いコミュニケーションへの旅を今日から始めましょう!